1 in 3 of all Google’s searches are for local businesses which is a huge opportunity for savvy business owners – if marketing dollars are spent in the right place.
Pay per click (PPC) marketing is one of the most targeted, and highest converting forms of advertising that a local business has in it’s marketing tool box.
It allows a businesses to advertise their products and services to people at the exact moment that they are actively searching for or researching those particular products or services.
It can also reach more people than the Yellow Pages, is more traceable, and costs a lot less than printing out thousands of fliers.
Setting up a PPC campaign on Google Adwords can be an extremely effective way to attract new customers to any local business…if it is set up the right way.
An incorrectly set-up campaign can:
- Target customers who aren’t in your city or state
- Waste your advertising budget
- Bring the wrong type of customer to your website
- Run through your ad budget quickly
The key for any good local Adwords campaign is to have your ads displayed to your potential customers at the right time and in the right place. This guide will show you how to do that the right way.
The key to Google Adwords is RELEVANCE.
“Google rewards you for being relevant, and they let people who are searching vote for you. If your ad gets clicked on, it’s relevant. If it doesn’t, it’s not. It’s that simple.” – Perry Marshall
How Google Adwords Campaigns are Structured
The first step in creating an excellent local PPC campaign is to get an understanding of how campaigns are structured within Google Adwords.
Google Adwords is made up of four main sections:
1. Campaigns – Daily advertising budget is set at this level.
2. Ad Groups – Similar keywords based on a common theme.
3. Ads – The actual ads you see in the Google search results.
4. Keywords – The search terms that trigger your ads.
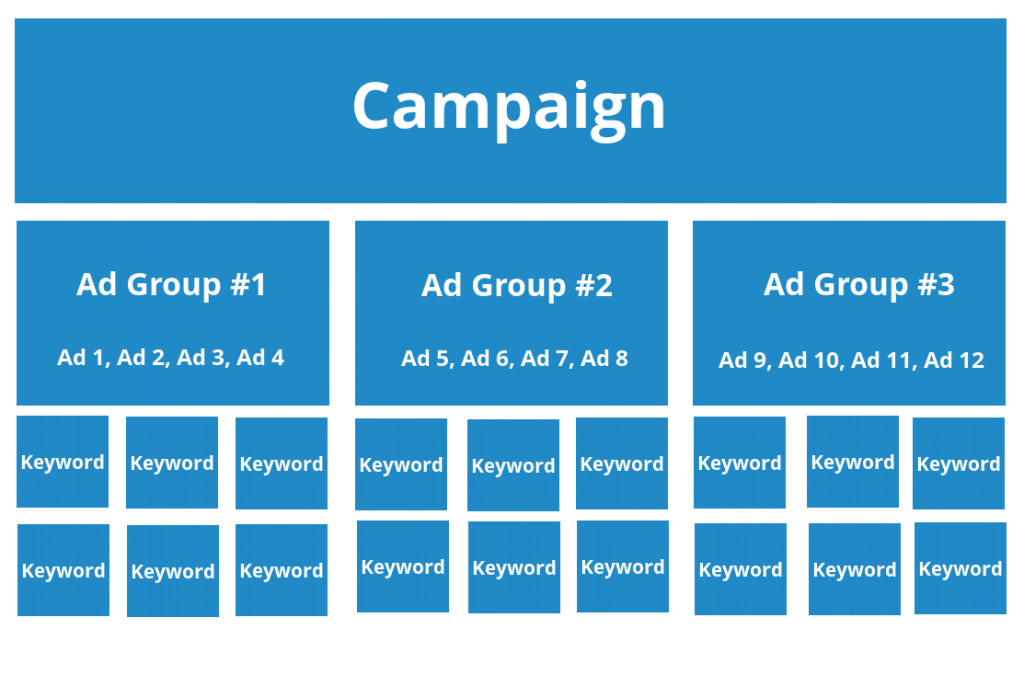
Once you have grasped the general structure of Google Adwords campaigns, the next step is to start planning one for your local business.
Steps to Setting Up a Profitable Local PPC Campaign
| 1. Keyword Research | 4. Add keywords | 7. Ad extensions |
| 2. Create campaigns | 5. Set match types | 8. Create landing pages |
| 3. Setup ad groups | 6. Write ads | 9. Install conversion tracking |
1. Keyword Research
The first step is to discover what your potential customers are searching for in your market. We have previously extensively covered how to do local keyword research – this exact same approach can be used for your local pay per click campaign.
Basically, all you need to do is create two lists. One list that contains the products and services your business offers, and a second list that has all the locations you service – cities, states, suburbs, postcodes and regions. Then you mix and match all these services and locations into a larger ‘master keyword list’.
Once you have used the Google keyword tool, brainstormed some relevant products and services, chosen some locations and then generated your ‘master keyword list’, you are ready to move onto the next step.
2. Create Campaigns
The next step of the local PPC campaign on Google Adwords is the campaign set up phase. It is extremely important that the correct settings and targeting parameters are selected at the campaign level otherwise you will waste your ad budget, and target customers in the wrong location. Head over to http://adwords.google.com and sign in using your Google Account – set one up if you don’t have one.
For a local business, there are generally two types of people looking for your business:
- A person who lives in your area, city or state who expects the results to be area-based only
- A person may not reside in your area at all – they may be out of town looking for your business.
Set Up Two Separate Campaigns
Campaign 1 – Geographical targeted campaign
This campaign is set up to target people searching from within your particular location. You would set geographical targeting to “melbourne” (instead of Australia) and use slightly broader keyword matching such as:
“florist”
“flowers delivered”
“same day flowers”
This campaign is set up to target people typing in searches that don’t include the physical location keyword in the search query.
Campaign 2 – Keyword Targeted Campaign
This campaign has a larger geographic region to target such as “Australia” – you are then segmenting your target market by the keywords they type in – these people may not reside in your target location but are still looking for services in that location. These will include searches typed in like:
“florist melbourne”
“flowers melbourne”
“same day flower deliver melbourne CBD”
The campaign settings for both should:
- Display ads on “search network only”
- Display ads on Google search ONLY (you don’t want your ads showing on other search engines)
- Have an acceptable daily budget set for both campaigns
3. Set Up Ad Groups
The next step is to create different ad groups within each campaign. The best way to do this is to group similar keywords from your keyword list into ‘buckets’ or ‘silos’ of similar themes.
Your ad groups may look like this:
| Florists Melbourne | Flowers Melbourne | Flower Delivery Melbourne |
|---|---|---|
| florists melbourne | flowers melbourne | flower delivery shop melbourne |
| florist melbourne | melbourne flower shop | fast flower delivery melbourne |
| best florist melbourne | flower stores melbourne | flower delivery melbourne |
Once you have segmented your keyword list into relevant ad groups, the next step is to add the entire keyword list into these groups.
You should also set bid prices for each of your ad groups at this stage. Bid prices can then then be updated once you get a better understanding of how competitive and expensive each of your target keywords after you have some performance data.
4. Add Keywords in Ad Groups
From the list you created in step one, add all of your keywords into these ad groups silos of tightly related terms. There can be any number of ad groups – it is important that all the keywords within any given ad group contain a similar theme.
Having keywords that are not closely related will result in low ad quality score, low click through rates, and poor overall performance.
Remember, what we said earlier – the key to Google Adwords is RELEVANCE. So keep these ad groups tight.
5. Set Match Type
The next step is to set ‘match types’ of keywords within each ad group.
There are 5 match types in Google Adwords:
1. Exact match
2. Phrase match
3. Broad match
4. Negative match
5. Broad modifier
I’ve covered keyword match types in greater depth previously which outlines what these match types mean, and how you use them to enhance your campaign.
I would recommend keeping the match types as [exact match] and “phrase match” to begin with, as broad match can result in your ads being displayed for searches that contain no relevance at all. Once you get some data after running the campaigns for a few weeks, then you can add in some broad match keywords – as long as you a tight negative keyword list.
For the example “florist melbourne” ad group, the keywords could be:
“florist melbourne”
[florist melbourne]
“florists in melbourne cbd”
[melbourne based florists]
Negative Match
A ‘negative’ keyword list contains a list of keywords that you do not want to trigger your ads. These could be words like “free”, “download”, “cheap” or any number of variations that don’t reflect the services you are offering.
This will help reduce the number of untargeted clicks and help improve your click through rate and your overall relevance (while saving your budget for the keywords that are going to convert into sales). This list is MANDATORY if you want to use any type of broad matching in your campaign.
6. Write Ads
Once you divided your campaigns into tightly related keyword ad groups, you are now ready to write the actual ads that are seen in Google when users type in your targeted keywords.
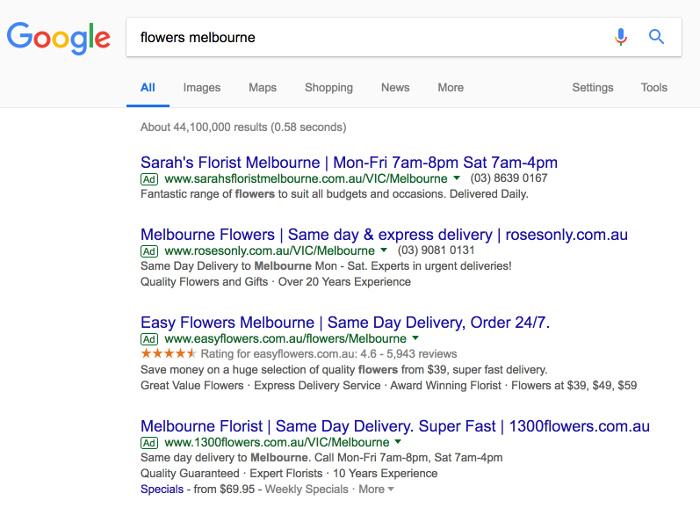
Ads are made up of 4 parts:
Headline – the most important element, use keywords to signify relevance.
URL – the website address and landing page (if you can fit).
Line 1 – your best features.
Line 2 – benefits and payoffs – Why choose you?
Put yourself in the shoes of your customer. Imagine you are your customer sitting in from of their computer. What do they type into the search bar? What do they hope comes up when they make a search?
Tips for writing ads:
- Capitalise important words
- Use emotive words
- Use keywords in headline
- ALWAYS be testing different versions of your ads (at least 2)
- Make the ad relevant to the keywords in your ad group
7. Ad Extensions
To make your ads more relevant and improve your click through rates, creating ad extensions is a must.
These enhance the regular AdWords ads and display additional information about your business, which gives your ads more opportunity to get noticed.
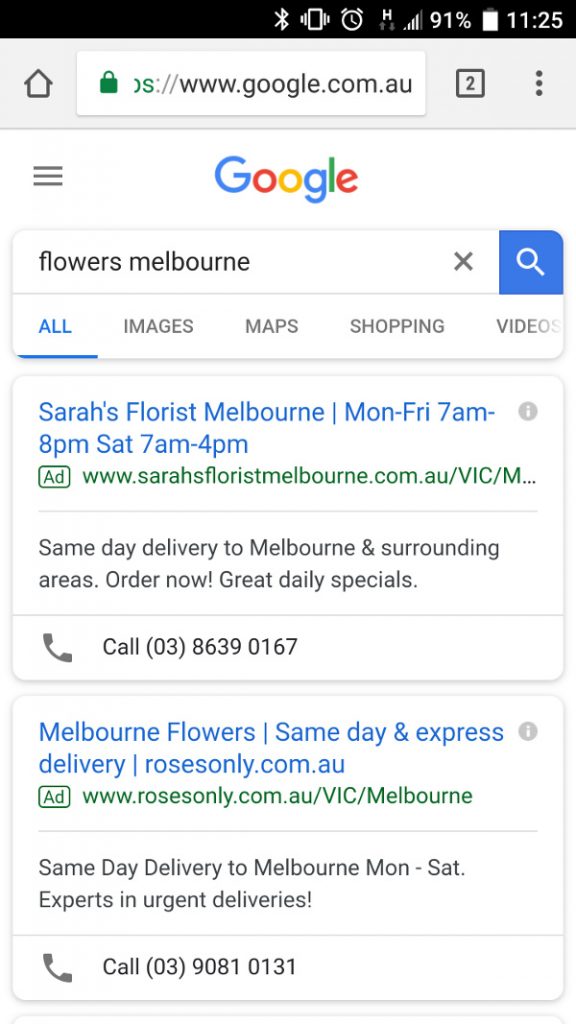
For your local campaign, the best ad extensions are:
- Location extensions – linking to your Google+ Local page or custom location address.
- Call extensions – great for people on mobile devices as they can ‘click to call’ your business through your ads.
- Sitelinks extensions – add in extra pages to link to such as “why buy from us” or “contact us”.
8. Landing Pages
After you have set up your campaigns, created similar themed ad groups and added in your various keywords, you now need to decide on what landing page you want to drive your visitors to.
As a general rule, you should NOT drive these visitors directly to your homepage. Ideally, each ad group should have a separate landing page with tailored content that reinforces the ad, and promotes your call to action.
What do you want them to do. Do you want your visitors to sign up? Call you? Fill out an enquiry form? Purchase something?
Here are a couple of excellent resources to help you put together your landing pages:
- 101 landing page optimisation tips
- 25 lead generation landing page examples
- Landing page tips from the pros
9. Conversion Code on Thank You Page
The final step in setting up your local PPC campaign on Google Adwords is make sure you are tracking your performance. Adwords offers conversion tracking which involves adding a piece of code onto your ‘thank you’ page.
This allows you to track the number of successful actions performed by visitors coming from your ads.
Google’s guide to setting up conversion tracking gives you everything you should need to know.
Test, Test, Test.
Congratulations! You’ve set up your first local PPC campaign.
Now you need to keep an eye on the performance of your ads, test different versions of your ads, try different bid prices and keyword match types.
Remember, the key to a good campaign is RELEVANCE – relevant ad copy for each keyword, relevant landing pages for keywords, and relevant and targeted copy. The more relevant your campaign is, the better your results will be.
